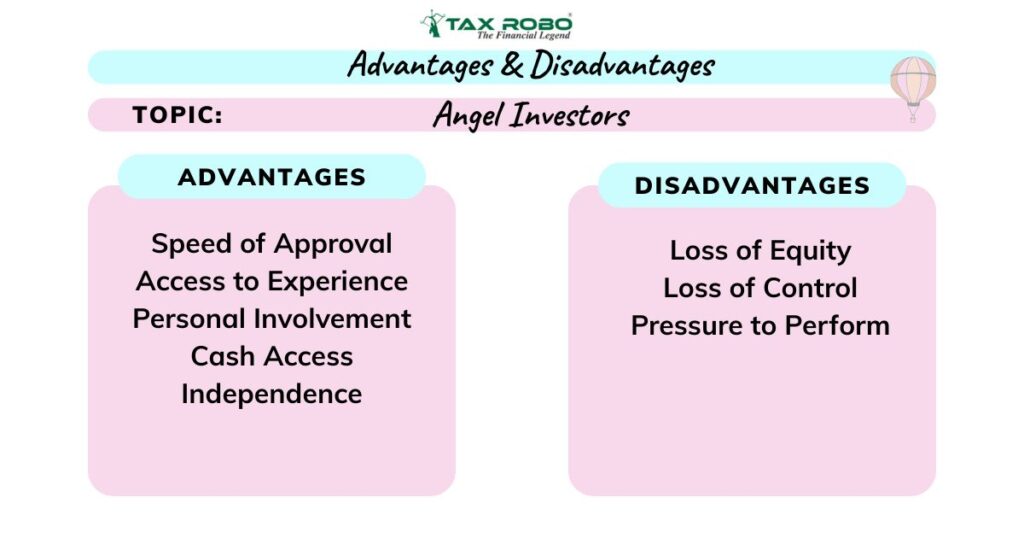
What are the advantages and disadvantages of taking on angel investment?
So, you have a brilliant business idea buzzing in your head, a spark that could ignite the next big thing in India. You’ve maybe even drafted a business plan, maybe built a small prototype. But then comes the big hurdle – money. Starting and scaling a business needs capital, often more than personal savings or loans from family can provide. This is where many aspiring Indian entrepreneurs first hear about ‘angel investors’. But what exactly does that mean, and is it the right path for your dream? Angel investment involves high-net-worth individuals (HNIs) investing their personal money into early-stage startups, typically in exchange for a share (equity) in the company. It’s becoming increasingly common in India’s vibrant startup ecosystem. This post aims to provide a balanced view by exploring the crucial advantages and disadvantages of angel investment, helping you decide if this funding route aligns with your vision.
Understanding Angel Investment in the Indian Context
Before weighing the pros and cons, it’s essential to understand who angel investors are in India and how this type of funding differs from other sources like venture capital. Getting clarity on this foundation will help you better appreciate the specific benefits and drawbacks discussed later.
Who are Angel Investors in India?
Angel investors in India are typically successful individuals with considerable personal wealth. They often fit one or more of these profiles:
- Successful Entrepreneurs: Individuals who have built and exited their own successful businesses. They understand the startup journey firsthand and often invest back into the ecosystem.
- Senior Corporate Executives: High-ranking professionals with deep industry knowledge, operational expertise, and valuable networks.
- High-Net-Worth Individuals (HNIs): Wealthy individuals looking to diversify their investments into potentially high-growth, albeit high-risk, assets like startups.
Their motivations vary. While a strong financial Return on Investment (ROI) is usually a primary goal, many angels are also driven by a passion for innovation, a desire to mentor emerging entrepreneurs, and the satisfaction of contributing to a startup’s success story. In India, many angels operate individually, but several prominent Angel Networks have emerged, pooling resources and expertise. Examples include the Indian Angel Network (IAN) and Mumbai Angels, which provide platforms for startups to connect with multiple investors simultaneously.
How Angel Investment Differs from Venture Capital (VC)
While both angels and VCs invest in startups, there are key differences:
| Feature | Angel Investors | Venture Capital (VC) Firms |
|---|---|---|
| Source of Funds | Invest their own personal wealth | Manage pooled funds from institutions (pension funds, etc.) |
| Investment Stage | Typically earlier (Pre-seed, Seed) | Usually later stages (Series A, B, C, Growth) |
| Investment Size | Generally smaller amounts (Lakhs to few Crores INR) | Significantly larger amounts (Multiple Crores INR) |
| Due Diligence | Can be less formal, quicker decision making | Extensive, formal due diligence process |
| Involvement Level | Often more hands-on mentorship and guidance | More formal governance (Board seats, reporting requirements) |
| Risk Appetite | Usually higher, comfortable with early-stage risk | Often prefer startups with proven traction or revenue |
Understanding these distinctions is vital because the expectations, deal terms, and level of involvement can differ significantly between angel investors and VCs.
The Upside: Key Advantages of Angel Investment in India
Now, let’s delve into the positive aspects. Securing angel funding can be transformative for an early-stage company. Here are some key benefits of angel investment for startups India:
Access to Crucial Seed Capital
This is often the most immediate and compelling advantage. Angel investment provides the essential seed capital needed to get a startup off the ground or through its initial critical phase. Bank loans are often difficult for early-stage, pre-revenue startups to secure due to the lack of collateral and high perceived risk. Personal funds might be limited. Angel money can bridge this gap, enabling founders to:
- Develop the product or service: Build the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) or refine an existing prototype.
- Hire key team members: Bring on essential talent in tech, marketing, or sales.
- Fund initial operations: Cover costs like office space (if needed), basic marketing, and legal setup.
- Achieve early milestones: Gain traction and validate the business model, making the startup more attractive for future funding rounds.
Without this initial injection of capital, many promising ideas might never see the light of day.
Valuable Mentorship and Strategic Guidance
Beyond just money, many angel investors bring invaluable “smart money” to the table. This refers to the non-monetary value they add through their experience and expertise. Particularly in India, many angels are seasoned entrepreneurs or industry veterans who have navigated the specific challenges and opportunities of the local market. They can offer:
- Strategic Direction: Help refine the business model, identify target markets, and set long-term goals.
- Industry Insights: Provide deep knowledge about market trends, competition, and potential pitfalls.
- Operational Advice: Offer guidance on building a team, setting up processes, managing finances, and scaling operations.
- Moral Support: Act as a sounding board and mentor, offering encouragement during the often-lonely and challenging startup journey.
This mentorship can significantly accelerate a startup’s learning curve and help avoid costly mistakes.
Access to Networks and Connections
A well-connected angel investor can open doors that would otherwise remain closed to a new startup. Their personal and professional networks can be a goldmine, providing introductions to:
- Potential Customers: Facilitating early sales and market validation.
- Strategic Partners: Helping forge collaborations that can accelerate growth.
- Key Suppliers: Securing better deals or access to essential resources.
- Future Investors: Providing warm introductions to Venture Capital firms or other later-stage investors when the time is right for subsequent funding rounds.
- Talent Pool: Recommending potential hires or advisors.
This network effect can dramatically enhance a startup’s reach and opportunities within the Indian business ecosystem.
Enhanced Credibility and Validation
Successfully securing funding from a reputable angel investor acts as a significant stamp of approval. It signals to the market that an experienced individual has vetted the business idea, the team, and the potential, and believes it’s worth backing with their own money. This validation can:
- Boost Confidence: Attract early customers who might be hesitant to engage with an unknown startup.
- Attract Talent: Make it easier to recruit skilled employees who see the angel’s involvement as a sign of stability and potential.
- Improve Negotiations: Strengthen the startup’s position when dealing with suppliers or partners.
- Pave the Way for Future Funding: Make the company more attractive to VCs and other institutional investors in later rounds.
In essence, angel backing lends credibility that can be hard for a fledgling company to build on its own.
Potentially More Flexible Terms (Compared to VCs)
While not always the case, angel investors, particularly those investing at the very earliest stages (pre-seed/seed), might sometimes offer slightly more founder-friendly or flexible terms compared to larger, institutional VCs. Because they are investing their own capital and often have personal motivations beyond pure ROI, they might be:
- More Understanding of Early Challenges: Potentially more patient if milestones take longer than expected.
- Simpler Term Sheets: Initial agreements might be less complex than multi-layered VC term sheets.
- Greater Flexibility on Control: While they will require rights, the governance structure might initially be less rigid than what VCs typically impose.
However, this is highly variable and depends heavily on the individual angel investor and the specific negotiation. Founders should never assume flexibility and must always scrutinize the term sheet carefully.
The Downside: Potential Disadvantages of Angel Investment India
While the advantages are compelling, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential drawbacks. Understanding these challenges of angel investment in India is vital before accepting funds.
Dilution of Ownership and Control
This is perhaps the most significant downside for founders. When you accept angel investment, you are typically selling equity, which is a percentage of ownership in your company. Key implications include:
- Reduced Ownership Stake: The founders’ percentage ownership decreases (dilution). If you give away 20% equity, you and your co-founders now own only 80% of the company you started. This dilution continues with subsequent funding rounds.
- Loss of Autonomy: Angel investors often require certain rights in exchange for their investment. This might include:
- Board Seats: Giving the investor a position on the company’s board of directors, allowing them direct input and voting rights on major decisions.
- Voting Rights: Specific rights allowing them to vote on critical matters like future fundraising, large expenditures, or changes in business direction.
- Information Rights: The right to receive regular financial and operational updates.
While investor input can be valuable, giving up equity and control means founders no longer have absolute say over their company’s destiny. Aligning visions early on is critical.
Pressure for Growth and Exit
Angel investors are not philanthropists; they expect a substantial Return on Investment (ROI) on their capital, often aiming for 10x or more over a period of 5-7 years. This return is typically realized through an exit event:
- Acquisition: The startup being bought by a larger company.
- Initial Public Offering (IPO): The startup listing its shares on a stock exchange (less common for early-stage angel exits but the ultimate goal for some).
This expectation creates inherent pressure on the founders to achieve rapid growth and actively work towards an exit scenario. This pressure might conflict with a founder’s vision if they prefer slower, more sustainable growth or wish to retain control of the company long-term without selling. The focus might shift from building a lasting business to building a sellable one.
Potential for Investor Interference (‘Smart Money’ vs. ‘Meddling’)
While mentorship is often cited as a key advantage, the line between helpful guidance (‘smart money’) and unwanted interference (‘meddling’) can sometimes blur. An overly involved angel might:
- Micromanage Operations: Attempt to dictate day-to-day decisions, undermining the founding team’s authority.
- Push Their Own Agenda: Prioritize strategies that benefit their ROI timeline over the company’s long-term health.
- Create Conflict: Disagreements on strategy or operations can lead to friction and distract the team.
It’s crucial for founders to assess an angel’s personality and expected level of involvement during the due diligence phase. Finding an investor whose style aligns with the founder’s needs and preferences is essential for a healthy working relationship. Mismatched expectations regarding involvement are a common source of founder-investor conflict.
Valuation Challenges at Early Stages
Determining the value of a startup, especially one with little or no revenue, is more art than science. This subjectivity can lead to valuation challenges:
- Founder vs. Investor Expectations: Founders naturally want a higher valuation to minimize equity dilution, while investors seek a lower valuation to maximize their potential return.
- Difficulty in Justification: Without significant traction or financial history, justifying a specific valuation can be tough, leading to protracted negotiations.
- Risk of Over-Dilution: If founders accept a very low valuation early on, they might give away too much equity, significantly impacting their ownership percentage after future funding rounds.
Disagreements over valuation are a common reason for angel investment deals falling through. Even if a deal is reached, an unfavorable valuation can have long-term consequences for the founders.
Finding the Right Angel Investor
Not all investment money is created equal. Finding any angel willing to invest might seem like a victory, but finding the right one is critical for long-term success. The challenges include:
- Identifying Potential Angels: Locating investors interested in your specific industry, stage, and geography.
- Assessing Fit: Evaluating if the angel’s expertise, network, and personality truly align with the startup’s needs and the founder’s working style.
- Due Diligence on the Investor: Just as investors perform due diligence on startups, founders should research potential angels. Talk to other founders in their portfolio, understand their reputation, and clarify their expectations regarding involvement and reporting.
Accepting money from the wrong angel – someone whose vision conflicts with yours, who lacks relevant expertise, or who has a reputation for being difficult – can be more detrimental than having no funding at all.
Weighing the Angel Investment Pros and Cons in India: Making the Right Choice
Ultimately, the decision to pursue angel investment requires careful consideration of your startup’s unique circumstances. It involves balancing the potential rewards against the inherent risks. Here’s how to approach making the right choice by weighing the angel investment pros and cons in India:
Assess Your Startup’s Specific Needs
Before actively seeking angel funding, take a hard look inwards:
- Funding Requirement: How much capital do you realistically need to reach your next significant milestone? Overestimating can lead to unnecessary dilution, while underestimating can leave you short.
- Capital vs. Strategic Value: Is your primary need just money, or is the mentorship, industry expertise, and network access offered by a ‘smart money’ angel equally or more critical? If you only need capital, other options like debt financing might be considered (though often harder for early stages).
- Tolerance for Dilution and Control: How comfortable are you, as a founder, with giving up a percentage of ownership and potentially some decision-making control? Be honest about your entrepreneurial style and long-term goals.
- Stage of Business: Are you truly at the ‘angel’ stage (idea, prototype, early traction), or are your needs better suited for friends/family funding, bootstrapping, or perhaps later-stage VC funding?
Answering these questions honestly will clarify whether angel investment is the appropriate path right now.
Conduct Due Diligence on Potential Angels
Don’t be so focused on securing investment that you neglect to thoroughly vet your potential investors. Treat it like hiring a long-term partner:
- Track Record & Expertise: Does the angel have experience in your industry or sector? What is their track record with previous investments? Have their portfolio companies succeeded?
- Reputation: Talk to other entrepreneurs who have received funding from this angel. What was their experience like? Are they known for being supportive, demanding, hands-off, or interfering? Online platforms and founder communities can be resources.
- Network Relevance: Does the angel’s network genuinely align with your needs (e.g., connections to relevant clients, partners, or follow-on investors in India)?
- Expectations & Involvement: Have open conversations about their expected level of involvement, reporting requirements, and communication style. Ensure there’s a mutual understanding and comfort level.
Choosing the right partner, not just the first available cheque, is paramount.
Understand the Term Sheet Thoroughly
The Term Sheet outlines the proposed terms of the investment. While often non-binding initially (except for clauses like confidentiality and exclusivity), it forms the basis for the final legal agreements. Pay close attention to:
- Valuation: Pre-money and post-money valuation determine how much equity the investor receives for their investment. Understand the calculation and its implications for dilution.
- Investment Amount & Type: The exact amount being invested and whether it’s straight equity, convertible notes, or another instrument.
- Board Seats & Control Provisions: Understand who gets seats on the board and what decisions require investor approval (veto rights).
- Liquidation Preferences: Defines how proceeds are distributed in an exit event (e.g., acquisition). Does the investor get their money back first (1x preference) before others receive anything? Are there participating preferences?
- Anti-Dilution Protection: Protects the investor’s ownership percentage in case of future ‘down rounds’ (funding rounds at a lower valuation).
- Information & Reporting Rights: Specifies the frequency and type of financial and operational updates the investor expects.
Crucially, seek expert legal advice before signing any Term Sheet or final investment agreements. An experienced startup lawyer can help you understand the nuances and negotiate terms that protect your interests. This is an area where professional guidance, like that offered by TaxRobo’s online CA consultation service, can be invaluable.
Legal & Financial Considerations (TaxRobo Expertise Area)
Importance of Proper Company Structure
Most angel investors in India prefer to invest in Private Limited Companies. This structure offers advantages like limited liability for owners, easier equity allocation, and a clearer framework for governance and compliance, which investors find reassuring. If your business is currently a proprietorship or partnership, you’ll likely need to convert or register it as a Private Limited Company before receiving investment. TaxRobo provides efficient company registration services tailored for startups. Also, learn more about Company Registration in India for additional insights.
Essential Legal Documents
Several key legal documents formalize the angel investment process:
- Term Sheet: As discussed, this outlines the basic terms and conditions of the proposed investment.
- Share Subscription Agreement (SSA): The formal contract where the investor agrees to subscribe to (buy) shares of the company at the agreed-upon terms, and the company agrees to issue those shares.
- Shareholders’ Agreement (SHA): A crucial document that governs the relationship between all shareholders (founders and investors). It details rights, obligations, transfer restrictions, exit clauses, information rights, board composition, reserved matters (requiring investor consent), and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Drafting and reviewing these complex documents requires legal expertise to ensure clarity and protect the interests of all parties involved. TaxRobo can connect you with legal professionals or review documents from a financial perspective via services like our online CA consultation.
Financial Due Diligence Preparedness
Angel investors, even if less formal than VCs, will conduct due diligence, especially on your financials. You need to be prepared:
- Clean Books: Maintain accurate and up-to-date accounting records. Messy financials are a major red flag for investors.
- Financial Projections: Develop realistic financial forecasts (revenue, expenses, cash flow) for the next 3-5 years, clearly outlining the assumptions behind them.
- Key Metrics: Track relevant Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for your business (e.g., user growth, customer acquisition cost, churn rate).
- Compliance Records: Ensure all statutory compliances (RoC filings, tax filings) are up-to-date.
TaxRobo’s accounting services and audit services can help ensure your financial house is in order and ready for investor scrutiny. Consider taking a step further by implementing efficient practices as discussed in Set Up An Accounting System for My Small Business.
Compliance Post-Investment
Receiving investment isn’t the end of the compliance journey; it’s often the beginning of more rigorous requirements:
- Registrar of Companies (RoC) Filings: Timely filing of annual returns, financial statements, and documentation related to share allotments with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA). You can find general information on the MCA portal.
- Statutory Registers: Maintaining updated registers of members, directors, charges, etc., as required by the Companies Act, 2013.
- Tax Compliance: Ensuring ongoing compliance with Goods and Services Tax (GST) and Income Tax regulations, including TDS (Tax Deducted at Source). TaxRobo offers dedicated GST services and Income Tax services.
- Investor Reporting: Adhering to the reporting requirements outlined in the SHA.
Failure to comply can lead to penalties and damage investor confidence. TaxRobo provides comprehensive ongoing compliance services to keep your startup on the right side of the law.
Conclusion
Angel investment can be a powerful lifeline for early-stage startups in India, providing not just essential capital but also invaluable mentorship, network access, and market credibility. The advantages of angel investment in India, particularly the infusion of seed funding and strategic guidance, can significantly accelerate a startup’s growth trajectory. However, it’s not a decision to be taken lightly. Founders must carefully weigh these benefits against the potential downsides, primarily the disadvantages of angel investment India, such as dilution of ownership and control, intense pressure for growth and exit, the risk of investor interference, and challenges in valuation and finding the right fit.
Ultimately, carefully evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of angel investment specific to your startup’s needs, stage, and long-term vision is crucial. Success often hinges on finding the right investor – one whose expertise, network, and expectations align with yours – and negotiating fair terms documented in robust legal agreements. Angel investment, when approached strategically and executed carefully with proper legal and financial diligence, can indeed be the catalyst that transforms a promising idea into a thriving business.
Ready to prepare your startup for investment? Navigating the complexities of funding, legal agreements, financial due diligence, and ongoing compliance can be overwhelming. TaxRobo offers expert services designed for startups, from company registration and legal document support to financial preparedness through accounting and auditing, plus seamless ongoing compliance management. Contact TaxRobo today for a consultation to ensure your startup is investment-ready and set up for success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How much equity do angel investors typically take in India?
Answer: There’s no fixed percentage. It varies greatly depending on factors like the startup’s valuation (pre-money), the amount invested, the stage of the company (idea vs. early traction), the industry sector, the perceived risk, and negotiation leverage. However, a typical range for seed-stage angel rounds in India might fall between 10% and 30% equity.
Q2: How can startups find angel investors in India?
Answer: Startups can find angel investors through various channels:
- Angel Networks: Platforms like Indian Angel Network (IAN), Mumbai Angels, LetsVenture, AngelList India connect startups with registered investors.
- Incubators & Accelerators: These programs often have strong connections with angel investors and host demo days.
- Startup Events & Conferences: Networking opportunities to meet potential investors.
- Personal & Professional Networks: Leverage connections through advisors, mentors, industry contacts, and LinkedIn.
- Cold Outreach (Less Effective): Directly contacting potential angels, though a warm introduction is always preferred.
Q3: What is the main difference between angel investment and a bank loan for a startup?
Answer: The core difference lies in Equity vs. Debt:
- Angel Investment (Equity): Angels provide capital in exchange for an ownership stake (equity) in the company. There’s no fixed repayment schedule or interest payment. The investor shares in the risk and potential reward (profit through exit).
- Bank Loan (Debt): Banks provide funds that must be repaid with interest over a fixed period. The bank does not take ownership. The startup bears the full burden of repayment regardless of its profitability. Banks typically require collateral or a strong financial history, making loans difficult for very early-stage startups.
Q4: What are the key legal documents involved in an angel round?
Answer: The primary legal documents in a typical angel investment round include:
- Term Sheet: A preliminary (usually non-binding) document outlining the key terms of the investment agreement.
- Share Subscription Agreement (SSA): The binding contract detailing the investor’s purchase of shares and the company’s issuance of those shares.
- Shareholders’ Agreement (SHA): The comprehensive agreement governing the relationship, rights, and obligations among all shareholders (founders and investors).
Q5: Do startups need to pay tax on the money received from angel investors?
Answer: Generally, funds received by a company through the issuance of shares (equity investment) are considered capital receipts, not revenue or income. Therefore, this amount is not typically subject to income tax for the startup receiving the funds. However, it’s crucial to ensure proper accounting treatment and compliance. Notably, Section 56(2)(viib) of the Income Tax Act (often referred to in the context of ‘Angel Tax’) can potentially tax the premium received on share issuance if the shares are issued above Fair Market Value (FMV) under certain conditions, particularly for investments from resident investors. Obtaining a proper valuation report and ensuring compliance is vital. Seeking expert advice from professionals like those at TaxRobo (TaxRobo Income Tax Service, TaxRobo Online CA Consultation Service) is highly recommended to navigate these complexities correctly.