How do Wealth Management Advisors Incorporate ESG Factors into Portfolios in India?
In today’s world, investing isn’t just about financial returns; it’s increasingly about aligning your money with your values. You might have heard terms like “sustainable investing” or “ESG” floating around. There’s a growing wave of interest in sustainable investing with ESG in India, capturing the attention of both everyday investors and businesses alike. But what does ESG actually mean? Simply put, ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance – a set of standards used to measure a company’s impact and ethical practices. The core question many investors are asking is: how do wealth management advisors incorporate ESG factors into investment portfolios? This is more than just a trend; understanding ESG is becoming crucial for Indian investors looking for long-term value, better risk management, and a way to ensure their investments reflect their personal principles. Integrating ESG is a significant part of current wealth management trends India, signaling a shift towards more conscious capitalism.
Understanding ESG Investing in the Indian Context
Before diving into how advisors use ESG, it’s important to understand what these factors represent and why they’re gaining traction specifically in India. ESG provides a framework to evaluate companies beyond traditional financial metrics, looking at their broader impact and sustainability.
What are ESG Factors? (Environmental, Social, Governance)
ESG criteria assess a company’s performance in three key areas:
- Environmental: This looks at a company’s impact on the planet. Key criteria include its carbon footprint, energy efficiency, water usage and conservation policies, waste management practices, pollution control, and adoption of renewable energy sources. For instance, in India, advisors might assess how companies manage water scarcity risks, a critical issue in many regions, or how effectively they are transitioning towards solar or other renewable energy sources, aligning with national priorities. Understanding these ESG factors in investment portfolio India helps gauge long-term resilience.
- Social: This focuses on how a company manages relationships with its employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities where it operates. Criteria include employee relations (fair wages, safe working conditions), diversity and inclusion policies, data privacy and security measures, customer satisfaction, ethical supply chain practices, and community engagement. Indian examples could involve scrutinizing labor practices in the manufacturing sector, evaluating how tech companies handle user data privacy amidst growing digital adoption, or assessing a company’s contribution to local community development.
- Governance: This deals with a company’s leadership, internal controls, shareholder rights, and corporate ethics. Key aspects include the structure and diversity of the board of directors, executive compensation policies, transparency in reporting, protection of shareholder rights, and overall business ethics and anti-corruption measures. In India, strong governance is crucial, especially considering past instances of corporate governance failures. Advisors look for companies with transparent practices and structures that align with regulations set by bodies like the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Why ESG Matters Now: The Growing Importance in India
ESG investing is moving from a niche interest to a mainstream consideration for several reasons:
- Investor Demand: A significant driver is the increasing demand from investors themselves, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, who prioritize ethical considerations alongside financial returns. They want their investments to reflect their values and contribute positively.
- Regulatory Push: Regulatory bodies are recognizing the importance of sustainability. SEBI’s mandate for Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) for the top listed companies is a major step. This requires companies to disclose their performance on various ESG parameters, providing investors with more standardized data. You can find details on SEBI’s requirements here: SEBI Master Circular for BRSR. This regulatory focus underscores the importance of ESG in portfolio management.
- Risk Management: Companies with poor ESG practices often face higher risks, including regulatory fines, reputational damage, operational disruptions due to environmental issues (like climate change impacts), and social unrest (like labor strikes). Incorporating ESG analysis helps identify and potentially avoid these risks.
- Potential for Performance: While not guaranteed, there’s growing evidence suggesting that companies with strong ESG performance may be more resilient, better managed, and positioned for long-term success. This focus on sustainability is a key element of modern wealth management trends India.
The Process: How Wealth Management Advisors Incorporate ESG Factors
So, how do advisors practically integrate these ESG considerations into your investment portfolio? It’s a systematic process designed to align your investments with both your financial objectives and your ESG preferences. Here’s a breakdown of the typical steps wealth management advisors incorporate ESG factors:
Step 1: Client Discovery and ESG Preference Assessment
The journey begins with a detailed conversation between you and your advisor. This isn’t just about your risk tolerance and financial goals anymore; it includes understanding your values and specific ESG priorities. Your advisor will discuss:
- Your level of interest in ESG investing.
- Which ESG aspects matter most to you (e.g., are you passionate about climate action, gender equality in the workplace, ethical corporate governance, or avoiding certain industries?).
- Whether you want to simply avoid ‘bad’ companies or actively seek out ‘good’ ones.
- Your expectations regarding the potential impact (financial and non-financial) of incorporating ESG.
This initial assessment is crucial for tailoring wealth management strategies with ESG in India that genuinely reflect your individual preferences as a small business owner or salaried professional.
Step 2: ESG Integration Strategies Used by Advisors
Once your preferences are clear, advisors employ various strategies for incorporating ESG factors in portfolios India. There isn’t a single “right” way; the approach often depends on the client’s goals, the advisor’s philosophy, and available investment options. Common strategies include:
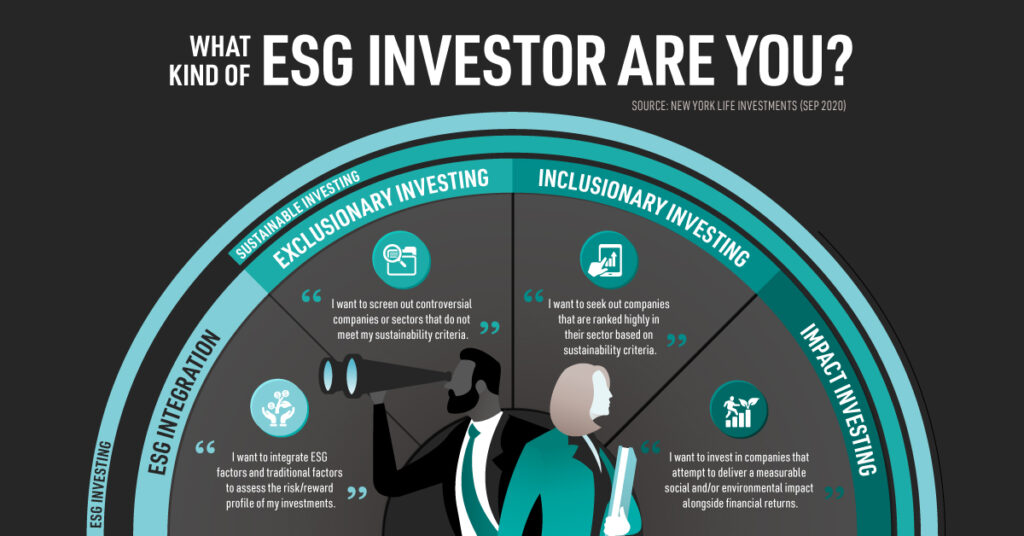
- Negative Screening (Exclusion): This is one of the oldest methods. It involves excluding specific sectors, industries, or companies from the portfolio that don’t meet certain ESG criteria or are involved in controversial activities. Common exclusions include tobacco manufacturers, weapons producers, thermal coal miners, or companies with severe human rights violations.
- Positive Screening / Best-in-Class: Instead of just excluding the worst performers, this approach actively selects companies that demonstrate strong ESG performance compared to their peers within the same sector. The idea is to invest in industry leaders who are managing ESG risks and opportunities effectively.
- ESG Integration: This is becoming increasingly common. Here, advisors systematically and explicitly include ESG factors into their traditional financial analysis and investment decision-making process for all investments. They assess how ESG issues might affect a company’s long-term performance, risk profile, and valuation, integrating these insights alongside metrics like P/E ratios or debt levels. This approach is central to comprehensive ESG portfolio management for Indian investors.
- Thematic Investing: This strategy focuses investments on specific sustainability themes aligned with ESG principles. Examples include portfolios centred around renewable energy, clean water technology, sustainable agriculture, education, or healthcare access. These funds aim to capitalize on growth opportunities within specific ESG-related sectors.
- Impact Investing: While often associated with private markets or high-net-worth individuals, the concept is relevant. Impact investments aim to generate specific, measurable positive social or environmental impact alongside a financial return. While less common in standard retail portfolios, thematic ESG funds often border on this concept.
| Strategy | Description | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Negative Screening | Excludes companies/sectors based on specific ESG criteria (e.g., tobacco, weapons). | Avoiding harm / controversial industries |
| Positive Screening | Selects companies leading in ESG performance within their industry. | Investing in the best ESG performers |
| ESG Integration | Systematically includes ESG analysis alongside traditional financial analysis. | Holistic risk/opportunity assessment |
| Thematic Investing | Focuses on specific ESG themes (e.g., clean energy, water). | Capitalizing on specific sustainability trends |
| Impact Investing | Targets measurable positive social/environmental impact alongside financial returns. | Generating specific positive outcomes |
Step 3: Research, Data Analysis, and Due Diligence
Incorporating ESG isn’t just about good intentions; it requires rigorous research and analysis. Advisors rely on various sources:
- ESG Rating Agencies: Firms like MSCI, Sustainalytics, Refinitiv, and others provide ESG ratings and reports on thousands of companies globally and in India. Advisors use these ratings as a starting point but often conduct their own analysis.
- Company Disclosures: With regulations like SEBI’s BRSR, companies in India are increasingly disclosing their ESG performance data through sustainability reports and annual filings.
- Proprietary Research: Many advisory firms develop their own frameworks and conduct in-house research to evaluate companies’ ESG credentials, going beyond third-party ratings.
A significant challenge is the lack of globally standardized ESG data and methodologies, which can sometimes lead to inconsistent ratings. Advisors must be diligent in evaluating the data sources and methodologies used. They also need to be wary of “greenwashing” – where companies overstate their ESG performance or environmental benefits. Verifying claims through multiple sources and qualitative assessment is key.
Step 4: Portfolio Construction and Implementation
Armed with client preferences and research insights, the advisor constructs the investment portfolio. This involves:
- Balancing ESG with Other Goals: ESG considerations are integrated alongside traditional factors like your risk tolerance, desired financial returns, investment horizon, and the need for diversification across asset classes and sectors.
- Selecting Investments: Based on the chosen strategy (screening, integration, thematic), the advisor selects specific investment instruments. In India, this could include:
- ESG Mutual Funds: A growing number of Asset Management Companies (AMCs) in India offer mutual funds specifically focused on ESG themes or employing ESG screening/integration.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ESG-focused ETFs that track specific sustainability indices are also becoming available.
- Direct Equity: For clients with larger portfolios or specific mandates, advisors might select individual stocks based on thorough ESG analysis.
- Diversification: Ensuring the portfolio remains well-diversified even after applying ESG criteria is crucial to manage risk.
Step 5: Ongoing Monitoring and Reporting
ESG investing is not a one-time setup. Advisors continuously monitor the portfolio’s holdings for both financial performance and adherence to ESG principles. This involves:
- Tracking Financial Returns: Assessing how the portfolio is performing against its financial benchmarks.
- Monitoring ESG Performance: Keeping track of the ESG ratings of portfolio companies, looking for significant changes or controversies. For thematic funds, tracking progress related to the theme (e.g., growth in renewable energy capacity).
- Regular Reporting: Providing clients with clear reports that show not only the financial performance but also the ESG characteristics of their portfolio and how it aligns with their stated goals. This transparency helps clients understand the tangible impact of their ESG portfolio management for Indian investors.
Finding the Right Advisor for ESG Investing in India
As ESG investing grows, more advisors are offering related services. However, expertise and approaches can vary significantly. Finding the right wealth management advisors in India who are genuinely skilled in ESG requires careful consideration.
Key Considerations When Choosing an Advisor
When evaluating potential advisors for your ESG investing needs, look for:
- Demonstrated ESG Expertise: Don’t just take their word for it. Ask about their specific experience, training, or certifications related to sustainable and ESG investing. How long have they been incorporating ESG factors?
- Transparency in Methodology: A good advisor should be able to clearly explain how they incorporate ESG factors – which strategies they use (screening, integration, etc.), what data sources they rely on, and how they measure ESG performance.
- Access to Indian ESG Products: Ensure they are knowledgeable about and have access to the relevant ESG mutual funds, ETFs, and other investment options available specifically within the Indian market.
- Alignment with Your Values: Choose an advisor whose philosophy on ESG and responsible investing resonates with your own personal financial goals and ethical principles. Do they understand your specific priorities?
Questions to Ask a Potential Wealth Management Advisor
To gauge an advisor’s suitability, consider asking these specific questions:
- “How do you incorporate ESG factors into your overall investment philosophy and portfolio construction process?”
- “What specific ESG data sources, research tools, and rating agencies do you rely on for your analysis, especially for Indian companies?”
- “Can you provide anonymized examples or case studies of ESG portfolio management for Indian investors with profiles similar to mine?”
- “How do you measure, monitor, and report on the ESG performance and impact of the portfolios you manage?”
- “What are the specific fees associated with your ESG-focused investment strategies compared to traditional strategies?”
- “How do you address the risk of ‘greenwashing’ in selecting ESG investments?”
- “How do you balance ESG considerations with traditional financial goals like diversification and returns?”
The depth and clarity of their answers will reveal their level of expertise and commitment to genuine ESG integration.
Benefits and Considerations for Indian Investors
Embarking on sustainable investing with ESG in India offers several potential advantages, but it’s also important to be aware of the challenges and nuances involved.
Potential Advantages of ESG Investing
- Alignment with Values: For many investors, the primary benefit is the ability to align their investments with their personal ethics and contribute towards positive environmental and social outcomes.
- Enhanced Long-Term Returns: While debated and not guaranteed, numerous studies suggest a positive or neutral correlation between strong ESG performance and corporate financial performance over the long term. This may be linked to better risk management, innovation, and operational efficiency in well-run, sustainable companies.
- Improved Risk Management: ESG analysis helps identify companies potentially exposed to environmental fines, regulatory crackdowns, reputational damage from social controversies, or governance failures. Avoiding these can help protect portfolio value.
- Positive Impact: Investing in companies or funds focused on sustainability allows you to directly support solutions to pressing challenges like climate change, inequality, and resource scarcity.
Potential Challenges and Things to Keep in Mind
- Defining and Measuring Impact: ESG is complex, and universally agreed-upon standards for measuring non-financial impact are still evolving. What one investor considers ‘good’ ESG performance might differ for another.
- “Greenwashing” Risk: The growing popularity of ESG has led to concerns about “greenwashing,” where companies or funds exaggerate their sustainability credentials. Diligent research by advisors is crucial to identify genuinely responsible investments.
- Data Challenges in India: While improving (thanks to initiatives like BRSR), the availability, consistency, and reliability of ESG data for all Indian companies can still be a challenge compared to developed markets.
- Limited Investment Universe: Applying strict negative screens might limit the range of available investments, which could potentially impact diversification if not managed carefully.
- Balancing Goals: There might be times when prioritizing strong ESG criteria could seem at odds with maximizing short-term financial returns or achieving specific diversification targets. A skilled advisor helps navigate this balance according to your overall objectives.
Conclusion
The way wealth management advisors incorporate ESG factors into investment portfolios is evolving rapidly, moving from a niche consideration to a core component of sophisticated financial planning in India. The process typically involves understanding your unique values and ESG priorities, applying specific strategies like screening or integration, conducting thorough research to avoid greenwashing, constructing a balanced portfolio, and providing ongoing monitoring and transparent reporting.
For Indian small business owners and salaried individuals, understanding the importance of ESG in portfolio management is increasingly vital. It offers a pathway to potentially enhance long-term returns, manage risks more effectively, and ensure your investments are not just growing your wealth but also contributing positively to the world around you. As wealth management trends India continue to embrace sustainability, discussing ESG options with your financial advisor is a crucial step in responsible financial planning.
Ensure your investment strategies, including those incorporating ESG, are supported by robust tax planning and compliance. Sound financial management goes hand-in-hand with meeting your legal obligations. Contact TaxRobo for expert assistance with your financial planning interface, tax filings, and compliance requirements, ensuring your financial journey is both profitable and compliant.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is ESG investing just a fad, or a long-term wealth management trend in India?
A: While ESG has gained significant popularity recently, it appears to be a durable, long-term trend rather than a short-lived fad. It’s driven by fundamental shifts including increasing investor awareness (especially among younger generations), growing regulatory pressure globally and in India (like SEBI’s BRSR mandate), a better understanding of sustainability-related risks (climate change, social inequality), and corporate responses to these pressures. These underlying drivers suggest ESG considerations are becoming embedded in investment analysis and wealth management trends India for the foreseeable future.
Q2: Will incorporating ESG factors in portfolios India lead to lower investment returns?
A: This is a common misconception. Numerous academic studies and meta-analyses have investigated the relationship between ESG factors and corporate financial performance. The majority find a neutral or positive correlation. Companies with strong ESG practices may exhibit better operational efficiency, improved risk management, enhanced brand reputation, and greater appeal to talent, potentially leading to sustainable long-term performance. However, it’s crucial to remember that past performance is not indicative of future results, and ESG investing, like all investing, involves risks. An advisor helps build a portfolio balancing ESG goals with financial return expectations.
Q3: How can I, as a small investor, verify if an investment is truly ESG-focused?
A: Verifying ESG claims requires some diligence. Look at the fund’s prospectus or offer document, which should detail its investment objective and strategy, including how it incorporates ESG. Check information provided by ESG rating agencies (like MSCI, Sustainalytics), but view these as one input, as methodologies differ. Rely on your wealth management advisor’s research and due diligence. For listed Indian companies, check their SEBI-mandated BRSR disclosures in their annual reports for detailed ESG performance data. Look for funds adhering to recognized ESG indices or holding relevant certifications, although these are still evolving in India.
Q4: Are there specific ESG mutual funds or ETFs easily available for retail investors in India?
A: Yes, the availability of ESG-focused mutual funds and ETFs for retail investors in India is steadily increasing. Several major Asset Management Companies (AMCs) now offer schemes that explicitly use ESG criteria for stock selection, employing strategies like exclusion, positive screening, or thematic investing (e.g., focusing on sustainable sectors). Wealth management advisors in India are well-versed in these products and can help identify suitable options based on your risk profile, investment goals, and specific ESG preferences.
Q5: What’s the difference between ESG integration and Impact Investing?
A: While related, they differ in intent and scope. ESG Integration involves systematically considering Environmental, Social, and Governance factors alongside traditional financial analysis for any investment to identify risks and opportunities that could affect performance. It’s broadly applied across a portfolio. Impact Investing, on the other hand, specifically targets investments made with the explicit intention to generate positive, measurable social and environmental impact alongside a financial return. Impact investments often focus on specific solutions (like affordable housing or renewable energy projects) and require rigorous impact measurement. While ESG integration is about managing risk and finding quality, impact investing is about actively seeking positive change.