Your Guide to Securing a Bank Loan for Startup Business in India
The dream of starting your own business burns bright for many in India. From innovative tech solutions to local service providers, the entrepreneurial spirit is thriving. However, turning that dream into reality often hits a common roadblock: securing the initial capital. While various funding avenues exist, understanding how to get a bank loan for startup business is crucial for many aspiring founders. This guide will walk you through the essentials of navigating the bank loan process in the Indian context, providing actionable insights for new entrepreneurs. Although securing funding can seem daunting, bank loans remain a significant consideration among startup funding options in India because they offer structured repayment plans and allow founders to retain full ownership, unlike equity funding. This guide is specifically tailored for aspiring entrepreneurs and newly established small businesses in India looking for clear, practical advice on financing their ventures through banking channels.
Understanding the Landscape: Why Choose a Bank Loan for Your Startup?
Opting for a bank loan for startup business comes with its own set of advantages and challenges that every entrepreneur should weigh carefully before proceeding. Banks are traditional financial institutions with established processes, which can be both a blessing and a hurdle. Understanding this landscape is the first step towards successfully securing the funds you need. It involves recognizing the potential benefits that align with your business goals while also being prepared for the inevitable scrutiny and requirements that banks impose, especially on new ventures with limited operating history.
Advantages of Bank Loans for Startups
Choosing a bank loan offers several distinct benefits for a fledgling enterprise. Firstly, compared to informal lenders or even some alternative financing options, bank loans often come with more competitive interest rates, particularly if you qualify under specific government schemes. This can significantly reduce the financial burden on your startup during its critical early stages. Secondly, successfully securing and repaying a bank loan helps build a positive credit history for your business entity right from the start. This track record is invaluable for future borrowing needs as your company grows. Thirdly, bank loans provide structured repayment schedules, allowing for better financial planning and budgeting predictability compared to more flexible, but sometimes uncertain, funding arrangements. Finally, and perhaps most importantly for many founders, taking a loan means you retain full ownership and control of your company, unlike equity financing where you trade shares for capital.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the advantages, securing a bank loan, especially a business loan for new company, presents significant challenges. Banks are inherently risk-averse, and startups are often perceived as high-risk borrowers due to their lack of track record and uncertain revenue streams. This leads to strict eligibility criteria that can be difficult for new businesses to meet. One of the biggest hurdles is the requirement for collateral or security. Many startups lack substantial assets to pledge, making traditional secured loans inaccessible. Furthermore, the loan approval process can be lengthy and bureaucratic, involving extensive documentation and due diligence, which can delay critical funding. Banks place immense importance on a strong, viable business plan with realistic financial projections – a document that requires significant effort and expertise to create effectively. This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge to navigate these challenges and increase your chances of success.
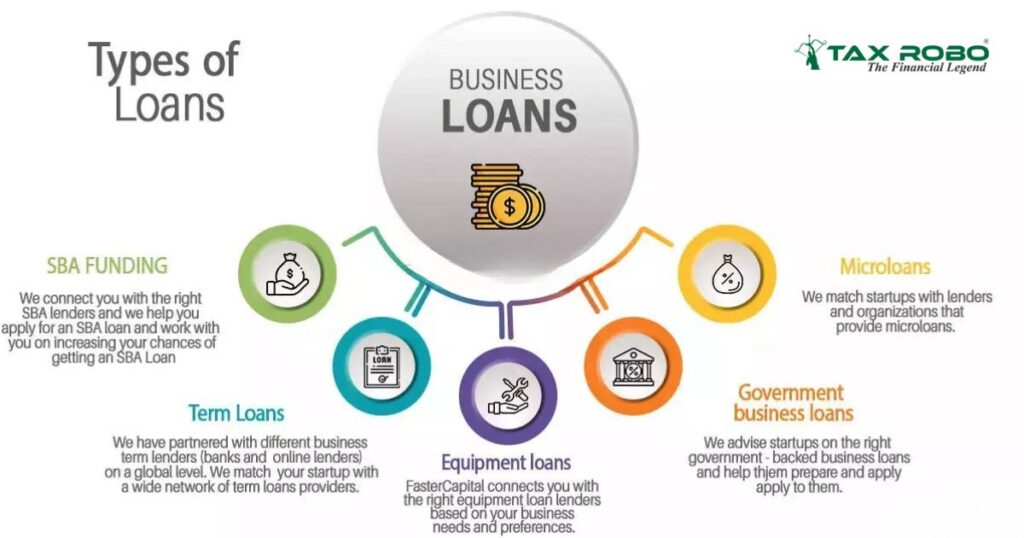
Exploring Different Loan Options for Startup Business in India
When seeking funding, it’s vital to understand the various loan options for startup business available through banks and government initiatives in India. Not all loans are structured the same way, and different types cater to different needs, from purchasing long-term assets to managing daily operational expenses. Furthermore, the Indian government actively promotes entrepreneurship through several specialized schemes designed to ease the funding bottleneck for new ventures, particularly those facing challenges with collateral or specific promoter demographics. Familiarizing yourself with these options will help you identify the most suitable path for your startup’s unique requirements.
Traditional Bank Loans
Banks offer several conventional loan products that startups can potentially access, though often with stringent requirements:
- Term Loans: These are standard loans provided for a fixed period (tenure) with a pre-defined repayment schedule (usually monthly EMIs). Term loans are typically used for capital expenditures like purchasing machinery, equipment, office space, or other long-term assets. The loan amount, interest rate, and tenure depend on the project’s viability, the promoter’s profile, and crucially, the availability of collateral or security. For startups, demonstrating repayment capacity through robust financial projections is key. To figure out how much capital might be required, read How Much Capital is Required to Start a Private Limited Company?
- Working Capital Loans: Unlike term loans used for fixed assets, working capital loans finance the day-to-day operational needs of a business. This includes paying salaries, purchasing inventory, managing receivables, and covering other short-term expenses. These loans often come in the form of a revolving credit line, such as an overdraft facility or cash credit limit, allowing businesses to draw funds as needed up to a sanctioned limit and repay when surplus cash is available. Interest is typically charged only on the amount utilized. Collateral is usually required, though the nature might differ from term loans (e.g., hypothecation of stock and receivables).
Key Government Loan Schemes for Startups
Recognizing the difficulties faced by new businesses, the Indian government has launched several government loan schemes for startups aimed at fostering entrepreneurship:
-
MUDRA Loan Scheme (Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana – PMMY):
- Purpose: This scheme targets micro and small non-corporate, non-farm sector income-generating activities. It aims to “fund the unfunded” by providing access to formal credit.
- Loan Categories: Loans are provided through banks, NBFCs, and MFIs under three categories based on the funding need and business stage:
- Shishu: Loans up to ₹50,000 (primarily for starting up)
- Kishor: Loans from ₹50,001 to ₹5 Lakh (for expansion/working capital)
- Tarun: Loans from ₹5 Lakh to ₹10 Lakh (for further expansion/asset purchase)
- Key Feature: Loans up to ₹10 Lakh under MUDRA do not require collateral.
- Actionable: Aspiring entrepreneurs should explore details and application procedures on the official Udyamimitra Portal or the MUDRA Website.
-
Stand-Up India Scheme:
- Purpose: This scheme specifically promotes entrepreneurship among Scheduled Caste (SC), Scheduled Tribe (ST), and Women entrepreneurs.
- Loan Details: It facilitates bank loans between ₹10 lakh and ₹1 crore per bank branch for setting up a greenfield (new) enterprise in manufacturing, services, or the trading sector.
- Key Feature: Aims to create at least one SC/ST borrower and one Woman borrower per bank branch. The loan includes working capital needs and margin money requirements might be eased.
- Actionable: Eligible entrepreneurs can check detailed guidelines and apply through the Stand-Up India Portal.
-
CGTMSE (Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises):
- Purpose: CGTMSE is not a direct lending scheme but rather a guarantee scheme that encourages banks and financial institutions to provide collateral-free credit to Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs), including startups.
- Mechanism: The trust provides a guarantee cover to the lending institution for credit facilities extended (up to ₹5 Crore per eligible borrower as per current norms) without requiring third-party guarantee or collateral security. Banks pay a fee to CGTMSE for this guarantee cover.
- Key Feature: Enables access to bank loans that might otherwise be rejected due to lack of collateral.
- Actionable: Startups applying for bank loans should inquire with the bank if the loan can be covered under the CGTMSE scheme. More information is available on the CGTMSE Website.
Bank-Specific Startup Programs
Beyond government schemes, many leading commercial banks in India have recognized the potential of the startup ecosystem and have launched their own specialized programs or dedicated cells to cater to the unique needs of new ventures. Banks like State Bank of India (SBI), HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, and others often have specific bank loan for startup India products. These programs might offer slightly relaxed eligibility norms (though still rigorous), dedicated relationship managers, faster processing, or bundled services relevant to startups.
Actionable: It is highly recommended that entrepreneurs research the websites of major banks or visit local branches to inquire about specific startup loan schemes, eligibility criteria, interest rates, and documentation requirements. Comparing these offerings alongside government schemes provides a broader perspective on available funding options.
Eligibility Criteria for a Startup Business Loan India
Securing a startup business loan India hinges significantly on meeting the bank’s eligibility criteria. Banks meticulously evaluate several factors to assess the risk associated with lending to a new venture. Understanding these parameters beforehand allows entrepreneurs to prepare adequately and present their case more effectively. While specific requirements might vary slightly between banks and loan schemes (especially government-backed ones), some common factors are almost universally considered. For those seeking a business loan for new company, demonstrating potential and mitigating perceived risks through thorough preparation is paramount.
Common Factors Banks Evaluate
Banks typically assess the following key areas when reviewing a startup loan application:
-
Promoter’s Profile: The background of the founder(s) is heavily scrutinized. This includes:
- Age: Usually within a specific range (e.g., 21-65 years).
- Experience: Relevant industry or managerial experience lends credibility.
- Educational Background: Qualifications related to the business field can be advantageous.
- Credit Score (CIBIL Score): A high CIBIL score (typically 700+) for all promoters is often non-negotiable. It reflects personal creditworthiness and repayment history.
-
Business Plan Viability: This is arguably the most critical element for a startup loan. The business plan must be comprehensive, well-researched, and convincing. Banks look for:
- Clear explanation of the product/service and its Unique Selling Proposition (USP).
- Detailed Market Analysis: Target audience, market size, competition analysis.
- Sound Marketing and Sales Strategy.
- Realistic Revenue Projections and profitability analysis (typically for 3-5 years).
- Assessment of the Management Team’s capabilities.
- A clear roadmap for execution (Operations Plan).
-
Business Type and Registration: The legal structure of your business matters. Banks need proof of legal existence. Common structures include:
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership Firm
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
- Private Limited Company
- One Person Company (OPC)
Banks require relevant registration documents (e.g., Certificate of Incorporation, Partnership Deed, GST Certificate, Udyam Registration). Need help with registration? TaxRobo offers seamless Company Registration Services.
- Collateral/Security: As mentioned, this is often a major hurdle for startups. While traditional loans usually require tangible assets (property, equipment, fixed deposits) as security, government schemes like MUDRA (up to ₹10 Lakh) and loans covered under CGTMSE offer pathways for collateral-free funding. Be prepared to discuss security options or justify why your business qualifies for a collateral-free scheme.
- Promoter’s Contribution (Margin Money): Banks rarely finance 100% of the project cost. They expect the founders to invest a portion of their own funds, known as margin money or promoter’s contribution. This typically ranges from 10% to 25% of the total project cost. It demonstrates the promoter’s commitment and reduces the bank’s risk exposure.
- Business Vintage: This refers to how long the business has been operational. Naturally, this is a challenge for a business loan for new company. Banks prefer established businesses with a track record. For startups, banks rely heavily on the strength of the business plan, the promoter’s profile, and robust financial projections to compensate for the lack of operating history. Government schemes are specifically designed to address this gap.
Essential Documentation: Preparing Your Loan Application
A well-organized and complete set of documents is fundamental to a smooth loan application process. Banks require extensive paperwork to verify the identity of the promoters, the legal existence of the business, the viability of the project, and the projected repayment capacity. Gathering these documents meticulously beforehand can significantly speed up the evaluation process and prevent unnecessary delays or rejections due to incomplete information. Think of the documentation phase as building the evidence to support the claims made in your business plan.
Standard Checklist for a Startup Loan Application
While the exact list might vary slightly depending on the bank, the loan type, and the business structure, here’s a standard checklist of documents typically required for a startup loan:
-
Identity & Address Proof (Promoters/Directors/Partners):
- PAN Card (mandatory)
- Aadhaar Card
- Passport
- Voter ID Card
- Driving License
- Recent Passport-sized Photographs
-
Business Address Proof:
- Latest Utility Bill (Electricity, Telephone)
- Rent Agreement (if premises are rented)
- Property Ownership documents (if owned)
-
Business Registration Documents:
- Certificate of Incorporation (for Companies)
- Memorandum of Association (MoA) & Articles of Association (AoA) (for Companies)
- Partnership Deed (for Partnership Firms/LLPs)
- LLP Agreement (for LLPs)
- GST Registration Certificate
- Udyam Registration Certificate (MSME Registration)
- Shop & Establishment Act License (if applicable)
- Other industry-specific licenses/registrations.
(TaxRobo can assist with various registrations, including GST Registration and Company Incorporation.)
-
Detailed Business Plan:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Market Opportunity Analysis
- Products/Services Description
- Marketing & Sales Strategy
- Operations Plan
- Management Team Profile
- Financial Projections: Projected Profit & Loss Statement, Cash Flow Statement, Balance Sheet (typically for the next 3-5 years). Break-even analysis. Funding requirements and utilization plan.
-
Financial Documents:
- Projected Financials: (Mandatory for startups as historical data is unavailable). Must be detailed and justifiable.
- Bank Account Statements: Personal bank statements of all promoters/directors for the last 6 to 12 months.
- Income Tax Returns (ITR): Personal ITRs of promoters/directors for the last 2-3 assessment years, along with computation of income.
- Net Worth Statements: Statements detailing the assets and liabilities of the promoters/guarantors.
-
Quotation for Assets:
- Proforma Invoices or Quotations for machinery, equipment, or other assets to be purchased using the loan amount.
-
Loan Application Form:
- The bank’s prescribed loan application form, duly filled and signed by the authorized signatory.
Actionable: Create a physical or digital folder and systematically gather all required documents. Ensure all copies are clear, legible, and up-to-date. Double-check every detail before submission, as discrepancies can lead to delays or rejection.
How to Get a Startup Business Loan: The Application Process Demystified
Understanding how to get a startup business loan involves knowing the typical sequence of steps from initial planning to final fund disbursement. While minor variations exist between banks, the core process remains largely consistent. Being aware of these stages helps you anticipate requirements, manage timelines, and navigate the journey more effectively. It transforms the application from a daunting task into a structured process with clear milestones.
Step 1: Craft a Compelling Business Plan
This cannot be emphasized enough – your business plan is the cornerstone of your loan application. It’s your primary tool to convince the bank of your venture’s potential and your ability to manage it successfully. Invest significant time and effort in developing a comprehensive, realistic, and well-researched plan covering all aspects mentioned earlier (market, operations, management, financials). It should clearly articulate your vision, strategy, and, crucially, how the loan will be utilized and repaid.
Step 2: Research and Select the Right Bank/Scheme
Don’t just walk into the nearest bank. Research various banks and financial institutions. Compare their specific startup loan products, interest rates, processing fees, repayment terms, and collateral requirements. Critically evaluate different loan options for startup business, paying close attention to government schemes like MUDRA, Stand-Up India, and the potential for CGTMSE coverage, as these might offer more favorable terms or relax collateral requirements. Choose a bank and scheme that best aligns with your business needs and eligibility profile. For more detailed insights into choosing the right legal structure, consider reading Choosing the Right Legal Structure for Your Business.
Step 3: Gather and Organize All Documentation
Refer back to the detailed checklist provided earlier. Systematically collect and organize every required document. Ensure all proofs are valid and current, financial statements are accurate, and registration papers are in order. Create copies for your records before submitting the originals (if required) or uploads. An incomplete or disorganized application is a common reason for delays and rejection. Accuracy and completeness are key.
Step 4: Submit the Application
Once your business plan is ready and all documents are gathered, complete the bank’s official loan application form accurately and truthfully. Submit the form along with the entire set of supporting documents through the bank’s preferred channel – this could be online via their portal or offline at a branch. Always keep a copy of the submitted application form and the acknowledgment receipt provided by the bank.
Step 5: Bank Evaluation and Due Diligence
After submission, the bank begins its evaluation process. This involves several stages:
- Initial Screening: Checking for completeness of documents and basic eligibility.
- Credit Appraisal: Assessing the promoter’s creditworthiness (CIBIL score check) and the financial viability presented in the business plan. Bank officials will analyze your projected financials, assumptions, and repayment capacity.
- Business Plan Review: Detailed scrutiny of your market analysis, operational strategy, and management team.
- Interaction/Interview: You may be called for meetings or interviews with credit managers to discuss your proposal, clarify doubts, and assess your understanding and commitment.
- Site Visit (Potential): For certain loans or larger amounts, the bank might conduct a visit to your proposed or existing business premises.
Be prepared to answer questions clearly and confidently during this stage. Promptly provide any additional information requested by the bank.
Step 6: Loan Sanction and Disbursement
If the bank is satisfied with its due diligence and perceives the proposal as viable, it will issue a Sanction Letter. This letter outlines the terms and conditions under which the loan is approved, including:
- Loan Amount Sanctioned
- Interest Rate (fixed or floating)
- Loan Tenure and Repayment Schedule (EMI)
- Processing Fees and other charges
- Collateral/Security requirements (if any)
- Other specific conditions precedent to disbursement.
Review the sanction letter very carefully before accepting it. If you agree to the terms, sign and return the acceptance copy. Following this, you’ll need to complete the final loan agreement documentation and fulfill any pre-disbursement conditions (like depositing margin money, creating security, etc.). Once all formalities are completed, the loan amount will be disbursed either directly to your bank account or sometimes directly to the supplier/vendor (in case of asset purchase).
Tips for Improving Your Chances of Loan Approval
While the loan application process is rigorous, especially for startups, there are several proactive steps you can take to significantly enhance your chances of securing approval. Banks look for preparedness, credibility, and reduced risk. Focusing on strengthening these aspects can make a substantial difference in how your application is perceived. Remember, the goal is to present your startup not as a gamble, but as a well-thought-out investment opportunity for the bank.
Strengthen Your Business Plan
Your business plan needs to be more than just an idea on paper; it must be a robust, data-driven document. Ensure your market research is thorough, your competitive analysis is realistic, and your financial projections are well-reasoned and backed by logical assumptions. Clearly articulate your revenue model, cost structure, and path to profitability. Avoid overly optimistic or vague statements. A plan that demonstrates a deep understanding of the market and realistic financial foresight inspires confidence.
Maintain a Good Credit Score
The personal CIBIL score of the promoters is a critical factor. Banks view it as an indicator of financial discipline and creditworthiness. Before applying for a loan, check your CIBIL score and report. If it’s low (below 700-750), take steps to improve it by paying existing dues on time and managing your personal credit responsibly. A strong credit history significantly boosts your credibility.
Show Promoter Contribution
Banks are more comfortable lending when the founders have their own skin in the game. Clearly demonstrating your promoter’s contribution (margin money) shows commitment and confidence in your own venture. It also reduces the bank’s overall exposure. Ensure you have arranged for your share of the funding and clearly mention it in your application and financial plan.
Be Prepared for Questions
During the evaluation process, bank officials will likely have questions about your business plan, financials, market, and operational strategy. Anticipate potential questions and prepare clear, concise, and confident answers. Practice explaining your business model, revenue streams, and risk mitigation strategies. Being well-prepared for interviews or discussions demonstrates professionalism and competence.
Explore Government Schemes
Actively investigate if your startup qualifies for any government loan schemes for startups like MUDRA or Stand-Up India. If lack of collateral is a major hurdle, inquire specifically about coverage under the CGTMSE scheme. Leveraging these schemes can significantly improve your chances, especially if you meet their target criteria (e.g., micro-enterprise, SC/ST/Woman entrepreneur). Mention your eligibility for these schemes prominently in your application.
Consider Professional Help
Navigating the complexities of business registration, compliance, financial projections, and documentation can be overwhelming. Seeking assistance from professionals can significantly strengthen your application. For instance, TaxRobo offers expert services for Company Registration, GST Compliance, preparing accurate Financial Projections and Accounting, and ensuring all necessary documentation is in order. Professional support can lend credibility and ensure your application package is complete and compliant, significantly improving your loan prospects. Contact TaxRobo for Online CA Consultation to discuss your specific needs.
Conclusion
Securing a bank loan for startup business in India is undoubtedly a process that demands diligence, preparation, and patience. From understanding the various loan options for startup business, including vital government loan schemes for startups, to meticulously preparing your business plan and documentation, each step is crucial. Meeting the eligibility criteria, particularly demonstrating promoter credibility and project viability, is key to navigating the bank’s evaluation process successfully. Following the outlined steps – thorough research, crafting a compelling plan, organizing documents, and preparing for scrutiny – can demystify the procedure outlined in how to get a startup business loan.
While the journey requires significant effort, a bank loan remains a viable and often essential funding route for many Indian entrepreneurs aiming to turn their vision into reality. It provides capital while allowing founders to retain ownership and build business credit. Remember, thorough preparation is your greatest asset. Start your planning today, explore all available avenues, and don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance. For expert assistance with company registration, compliance, financial documentation, and making your loan application stronger, consider reaching out to TaxRobo. We are here to support your entrepreneurial journey.
FAQ Section
Frequently Asked Questions about Bank Loans for Startups
-
Q1: Can I get a
business loan for new companywithout any collateral in India?
Answer: Yes, obtaining a collateral-free business loan for new company is possible in India, primarily through specific government initiatives. The MUDRA loan scheme offers collateral-free loans up to ₹10 lakh for micro and small enterprises. Additionally, loans covered under the CGTMSE scheme allow banks to lend without collateral (up to ₹5 Crore currently), as the scheme provides a guarantee to the bank. However, eligibility for these schemes is strict, and a very strong business plan and promoter profile are essential. Traditional bank loans outside these schemes usually require substantial collateral. -
Q2: What is the typical interest rate for a
startup business loan India?
Answer: Interest rates for a startup business loan India can vary significantly. They depend on numerous factors including the specific bank, the chosen loan scheme (government schemes often have subsidized or lower rates), the loan amount, repayment tenure, the promoter’s creditworthiness (CIBIL score), the perceived risk of the business, and prevailing market rates (like the MCLR – Marginal Cost of Funds based Lending Rate). Generally, you might expect interest rates to range anywhere from 10% to 18% per annum, but it’s crucial to get current quotes directly from lenders for accurate comparison. -
Q3: How long does it take to get a
bank loan for startup businessapproved?
Answer: The approval timeline for a bank loan for startup business varies widely. Loans under schemes like MUDRA, especially the smaller Shishu category, might be processed relatively quickly, potentially within 2-4 weeks, assuming all documentation is perfect. However, larger loans, traditional bank loans requiring significant due diligence, or loans under schemes like Stand-Up India or those needing CGTMSE approval can take considerably longer, often ranging from 1 to 3 months or even more after the complete application is submitted. Factors like bank workload, application completeness, and complexity of the proposal influence the timeline. -
Q4: My business isn’t registered yet. Can I still apply for a
bank loan for startup India?
Answer: While you can certainly *start* the process of preparing your business plan and even initiate preliminary discussions with banks before formal registration, most banks will require proof of business registration (as a Proprietorship, Partnership, LLP, Private Limited Company, etc.) before the final loan sanction and disbursement. Business registration documents are a mandatory part of the application checklist. Therefore, it’s advisable to get your business registered concurrently with or shortly after finalizing your business plan. TaxRobo offers quick and efficient Company Registration services to help you get started. -
Q5: What are other
startup funding options in Indiaif my bank loan is rejected?
Answer: If your bank loan application is unsuccessful, several other startup funding options in India exist. Consider exploring:- Angel Investors: High-net-worth individuals who invest their personal funds in exchange for equity.
- Venture Capital (VCs): Firms that invest larger amounts in startups with high growth potential, usually scalable tech companies, in exchange for significant equity.
- Bootstrapping: Self-funding the business using personal savings or initial revenues.
- Crowdfunding: Raising small amounts of capital from a large number of people, typically via online platforms.
- Incubators and Accelerators: Programs that offer seed funding, mentorship, and resources, often in exchange for equity.
- NBFCs (Non-Banking Financial Companies): These institutions may have different lending criteria than banks, sometimes offering loans more readily but potentially at higher interest rates.
- Personal Loans: While generally not advisable for large business funding due to higher rates and personal liability, it’s sometimes used for very small initial capital needs.